|
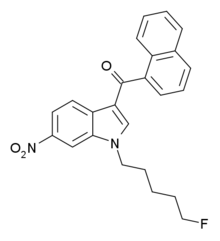
AM-1235
AM-1235 (1-(5-fluoropentyl)-3-(naphthalen-1-oyl)-6-nitroindole) is a drug that acts as a potent and reasonably selective agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1. PharmacologyPharmacodynamicsAM-1235 is a cannabinoid receptor agonist with Ki of 1.5 nM at CB1 compared to 20.4 nM at CB2.[1] While the 6-nitro substitution on the indole ring reduces affinity for both CB1 and CB2 relative to the unsubstituted parent compound AM-2201, CB2 affinity is reduced much more, resulting in a CB1 selectivity of around 13 times.[2] This is in contrast to other related compounds such as AM-1221 where a 6-nitro substitution instead confers significant selectivity for CB2.[3] Pharmacokinetics
AM-1235 metabolism differs only slightly from that of JWH-018. AM-1235 N-dealkylation produces fluoropentane instead of pentane (or plain alkanes in general). It has been speculated that the fluoropentane might function as an alkylating agent or is further metabolized into toxic fluoroacetic acid. This is not true since fluoroalkanes do not act as alkylating agents under normal conditions and uneven fluoroalkane chains metabolize into substantially less toxic fluoropropanoic acid.[4][5] Legal statusIn the United States, all CB1 receptor agonists of the 3-(1-naphthoyl)indole class such as AM-1235 are Schedule I Controlled Substances.[6] See also
References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||