|
Chemical compound
Pharmaceutical compound
Indacaterol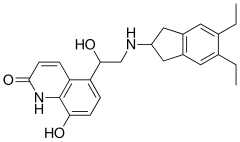 |  | |
| Trade names | Onbrez, Arcapta |
|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
|---|
| License data |
|
|---|
Pregnancy
category | |
|---|
Routes of
administration | Inhalation |
|---|
| ATC code | |
|---|
|
| Legal status |
|
|---|
|
5-[2-[(5,6-Diethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-yl)amino]-1-hydroxyethyl]-8-hydroxyquinolin-2(1H)-one
| | CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| KEGG | |
|---|
| ChEBI | |
|---|
| ChEMBL | |
|---|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.218.577  |
|---|
|
| Formula | C24H28N2O3 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 392.499 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
O=C4/C=C\c1c(c(O)ccc1[C@@H](O)CNC3Cc2cc(c(cc2C3)CC)CC)N4
|
InChI=1S/C24H28N2O3/c1-3-14-9-16-11-18(12-17(16)10-15(14)4-2)25-13-22(28)19-5-7-21(27)24-20(19)6-8-23(29)26-24/h5-10,18,22,25,27-28H,3-4,11-13H2,1-2H3,(H,26,29)/t22-/m0/s1  Y YKey:QZZUEBNBZAPZLX-QFIPXVFZSA-N  Y Y
|  N N Y (what is this?) (verify) Y (what is this?) (verify) |
Indacaterol is an ultra-long-acting beta-adrenoceptor agonist[5] developed by Novartis. It needs to be taken only once a day,[6] unlike the related drugs formoterol and salmeterol. It is licensed only for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (long-term data in patients with asthma are thus far lacking). It is delivered as an aerosol formulation through a dry powder inhaler.
Medical uses
A Cochrane review found benefit in lung function in people with COPD at least as good as that seen with twice-daily long-acting beta2-agonists.[7]
History
It was approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) under the brand name Onbrez Breezhaler on November 30, 2009,[8] and by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), under the brand name Arcapta Neohaler, on July 1, 2011.[9][10] In 2016, Novartis licensed its U.S. commercial rights for Arcapta Neohaler to Sunovion Pharmaceuticals.[11]
References
- ^ "Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol) inhalation powder Initial U.S. Approval: 2011". DailyMed. 1 April 2020. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ "Onbrez Breezhaler EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ "Oslif Breezhaler EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ "Hirobriz Breezhaler EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2021.
- ^ Cazzola M, Matera MG, Lötvall J (July 2005). "Ultra long-acting beta 2-agonists in development for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 14 (7): 775–83. doi:10.1517/13543784.14.7.775. PMID 16022567. S2CID 11930383.
- ^ Beeh KM, Derom E, Kanniess F, Cameron R, Higgins M, van As A (May 2007). "Indacaterol, a novel inhaled beta2-agonist, provides sustained 24-h bronchodilation in asthma". Eur. Respir. J. 29 (5): 871–8. doi:10.1183/09031936.00060006. PMID 17251236.
- ^ Geake, James B (2015). "Indacaterol, a once-daily beta2-agonist, versus twice-daily beta2-agonists or placebo for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease". Reviews. 1 (3): CD010139. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010139.pub2. PMC 6464646. PMID 25575340.
- ^ European Public Assessment Report for Onbrez Breezhaler Archived 2010-01-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "FDA approves Arcapta Neohaler to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease" (Press release). U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2011-07-01. Archived from the original on 2011-07-03. Retrieved 2011-07-02.
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Arcapta Neohaler (indacaterol maleate) NDA #022383". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 13 August 2013. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Faulkner, Sarah (22 December 2016). "Sunovion, Novartis ink licensing deal for inhaled COPD drugs". Drug Delivery Business.
|
|---|
| α1 | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- Abanoquil
- Ajmalicine
- Alfuzosin
- Anisodamine
- Anisodine
- Atiprosin
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., brexpiprazole, clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, risperidone)
- Benoxathian
- Beta blockers (e.g., adimolol, amosulalol, arotinolol, carvedilol, eugenodilol, labetalol)
- Buflomedil
- Bunazosin
- Corynanthine
- Dapiprazole
- Domesticine
- Doxazosin
- Ergolines (e.g., acetergamine, ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, lisuride, nicergoline, terguride)
- Etoperidone
- Fenspiride
- Hydroxyzine
- Indoramin
- Ketanserin
- L-765,314
- mCPP
- Mepiprazole
- Metazosin
- Monatepil
- Moxisylyte
- Naftopidil
- Nantenine
- Neldazosin
- Niaprazine
- Niguldipine
- Pardoprunox
- Pelanserin
- Perlapine
- Phendioxan
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Phentolamine
- Phenylpiperazine antidepressants (e.g., hydroxynefazodone, nefazodone, trazodone, triazoledione)
- Piperoxan
- Prazosin
- Quinazosin
- Quinidine
- Silodosin
- Spegatrine
- Spiperone
- Talipexole
- Tamsulosin
- Terazosin
- Tiodazosin
- Tolazoline
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, maprotiline, mianserin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline, clomipramine, doxepin, imipramine, trimipramine)
- Trimazosin
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, loxapine, thioridazine)
- Urapidil
- WB-4101
- Zolertine
|
|---|
|
|---|
| α2 | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- 1-PP
- Adimolol
- Amesergide
- Aptazapine
- Atipamezole
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., asenapine, brexpiprazole, clozapine, lurasidone, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, risperidone, zotepine)
- Azapirones (e.g., buspirone, gepirone, ipsapirone, tandospirone)
- BRL-44408
- Buflomedil
- Cirazoline
- Efaroxan
- Esmirtazapine
- Fenmetozole
- Fluparoxan
- Idazoxan
- Ketanserin
- Lisuride
- mCPP
- Mianserin
- Mirtazapine
- NAN-190
- Pardoprunox
- Phentolamine
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Piperoxan
- Piribedil
- Rauwolscine
- Rotigotine
- Setiptiline
- Spegatrine
- Spiroxatrine
- Sunepitron
- Terguride
- Tolazoline
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, loxapine, thioridazine)
- Yohimbine
|
|---|
|
|---|
| β | |
|---|
|
|

