|
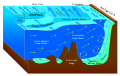
Deep ocean waterDeep ocean water (DOW) is the name for cold, salty water found in the deep sea, starting at 200 m (660 ft) below the surface of Earth's oceans. Ocean water differs in temperature and salinity. Warm surface water is generally saltier than the cooler deep or polar waters;[1] in polar regions, the upper layers of ocean water are cold and fresh.[2] Deep ocean water makes up about 90% of the volume of the oceans. Deep ocean water has a very uniform temperature, around 0–3 °C (32–37 °F), and a salinity of about 3.5% or, as oceanographers state, 35‰ (parts per thousand).[3] In specialized locations, such as the Natural Energy Laboratory of Hawaii, ocean water is pumped to the surface from approximately 900 m (3,000 ft) deep for applications in research, commercial and pre-commercial activities. DOW is typically used to describe ocean water at sub-thermal depths[clarify] sufficient to provide a measurable difference in water temperature. When deep ocean water is brought to the surface, it can be used for a variety of things. Its most useful property is its temperature. At the surface of the Earth, most water and air is well above 3 °C. The difference in temperature is indicative of a difference in energy. Where there is an energy gradient, skillful application of engineering can harness that energy for productive use by humans. The simplest use of cold water is for air conditioning: using the cold water itself to cool air saves the energy that would be used by the compressors for traditional refrigeration. Another use could be to replace expensive desalination plants. When cold water passes through a pipe surrounded by humid air, condensation results. The condensate is pure water, suitable for humans to drink or for crop irrigation. Via a technology called ocean thermal energy conversion, the temperature difference can be used to run a heat engine to generate electricity. Cold-bed agricultureA potential indirect use of cold ocean water is "cold-bed agriculture". During condensation or ocean thermal energy conversion operations, the water does not reach ambient temperature, because a certain temperature gradient is required to make these processes viable. The water leaving those operations is therefore still colder than the surroundings, and a further benefit can be extracted by passing this water through underground pipes, thereby cooling agricultural soil. This reduces evaporation, and even causes water to condense from the atmosphere.[4] This allows agricultural production where crops would normally not be able to grow. This technique is sometimes referred to as "cold agriculture"[5] or "cold-bed agriculture".[6] See alsoReferences
|