维基百科 中的醫學内容
仅供参考 ,並
不能 視作專業意見。如需獲取醫療幫助或意見,请咨询专业人士。詳見
醫學聲明 。
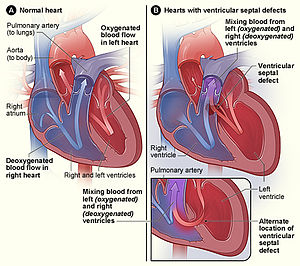
先天性心臟病 (congenital heart defect , CHD)简称先心病 ,是婴儿出生 时就存在的心血管 结构和功能的异常[ 2] 心脏 和大血管 发育异常或发育障碍,以及出生后应退化 的组织未退化所造成的心血管局部解剖结构异常。
先心病有其他异名 ,如:先天性心脏缺陷 (congenital heart defect)、先天性心脏异常 (congenital heart anomaly)、先天性心血管畸形 (congenital cardiovascular malformation/deformity),且根据血流动力学 结合病理生理变化,先天性心脏病可分为发绀型或者非发绀型,也可根据有无分流 分为三类:无分流类、左至右分流类和右至左分流类。
先心病的徵象和症状隨心臟問題的種類而不同[ 3] [ 2] 發紺 、體重增加緩慢、以及容易疲倦[ 4] [ 4] [ 3] 心臟衰竭 [ 4]
先天性心臟病的成因大多未知[ 5] 懷孕 時期的感染(如德國麻疹 )、使用特定藥物或有毒物質(如酒精 或菸 ),而父母親也和此疾病有關連,如母親的營養不良或肥胖 [ 3] [ 6] [ 7] 唐氏症 、透納氏症 ,和馬凡氏症候群 [ 3] 發紺性心臟病 非發紺性心臟病 發紺 來分。[ 2] [ 2]
先天性心臟病可以透過接種德國麻疹 疫苗、含有碘 的鹽,及添加了葉酸 的某些食物製品,來達到部分的預防功效[ 2] [ 2] 心導管手術 或心臟外科手術 完成有效的治療[ 8] 心臟移植 [ 8] [ 2]
心臟疾病是最常見的先天缺陷 [ 3] [ 9] [ 9] [ 3] [ 7] [ 7] [ 3] [ 10]
先天心臟病發生率 2012 0-8
9-12
13-23
24-31
32-39
40-47
48-50
51-56
57-63
64-124
^ Hoffman JI, Kaplan S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. June 2002, 39 (12): 1890–900. PMID 12084585 doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(02)01886-7 ^ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 What Are Congenital Heart Defects? . National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011 [10 August 2015] . (原始内容存档 于2015-08-13). ^ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Shanthi Mendis; Pekka Puska; Bo Norrving; World Health Organization. Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control (PDF) . World Health Organization in collaboration with the World Heart Federation and the World Stroke Organization. 2011: 3, 60 [2016-01-20 ] . ISBN 978-92-4-156437-3存档 (PDF) 于2014-08-17). ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Congenital Heart Defects? . National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011 [10 August 2015] . (原始内容存档 于2015-07-27). ^ What Causes Congenital Heart Defects? . National,Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011 [10 August 2015] . (原始内容存档 于2015-07-08). ^ Dean, SV; Lassi, ZS; Imam, AM; Bhutta, ZA. Preconception care: nutritional risks and interventions.. Reproductive health. 26 September 2014,. 11 Suppl 3: S3. PMID 25415364 doi:10.1186/1742-4755-11-s3-s3 ^ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Milunsky, Aubrey. 1. Genetic Disorders and the Fetus: Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment . John Wiley & Sons. 2011 [2016-01-20 ] . ISBN 9781444358216存档 于2016-03-05). ^ 8.0 8.1 How Are Congenital Heart Defects Treated? . National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. July 1, 2011 [10 August 2015] . (原始内容存档 于2015-07-27). ^ 9.0 9.1 Global Burden of Disease Study 2013, Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet (London, England). 7 June 2015. PMID 26063472 doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4 ^ GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. . Lancet. 17 December 2014, 385 : 117–71. PMC 4340604 PMID 25530442 doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2