|
Valar
 The Valar (['valar]; singular Vala) are characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. They are "angelic powers" or "gods"[T 1] subordinate to the one God (Eru Ilúvatar). The Ainulindalë describes how some of the Ainur choose to enter the world (Arda) to complete its material development after its form is determined by the Music of the Ainur. The mightiest of these are called the Valar, or "the Powers of the World", and the others are known as the Maiar. The Valar are mentioned briefly in The Lord of the Rings but Tolkien had developed them earlier, in material published posthumously in The Silmarillion, especially the "Valaquenta" (Quenya: "Account of the Valar"), The History of Middle-earth, and Unfinished Tales. Scholars have noted that the Valar resemble angels in Christianity but that Tolkien presented them rather more like pagan gods. Their role in providing what the characters in Middle-earth experience as luck or providence is also discussed. Origin and actsThe creator Eru Ilúvatar first reveals to the Ainur his great vision of the world, Arda, through musical themes, as described in Ainulindalë, "The Music of the Ainur".[T 2] This world, fashioned from his ideas and expressed as the Music of Ilúvatar, is refined by thoughtful interpretations by the Ainur, who create their own themes based on each unique comprehension. No one Ainu understands all the themes that spring from Ilúvatar. Instead, each elaborates individual themes, singing of mountains and subterranean regions, say, from themes for metals and stones. The themes of Ilúvatar's music are elaborated, and each of the Ainur add harmonious creative touches. Melkor, however, adds discordant themes: He strives against the Music; his themes become evil because they spring from selfishness and vanity, not from the enlightenment of Ilúvatar.[T 2] 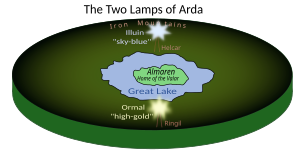 Once the Music is complete, including Melkor's interwoven themes of vanity, Ilúvatar gives the Ainur a choice—to dwell with him or to enter the world that they have mutually created. The greatest of those that choose to enter the world become known as the Valar, the 'Powers of Arda', and the lesser are called the Maiar. Among the Valar are some of the most powerful and wise of the Ainur, including Manwë, the Lord of the Valar, and Melkor, his brother. The two are distinguished by the selfless love of Manwë for the Music of Ilúvatar and the selfish love that Melkor bears for himself and no other—least of all for the Children of Ilúvatar, Elves and Men.[T 2] Melkor (later named Morgoth, Sindarin for "dark enemy") arrives in the world first, causing tumult wherever he goes. As the others arrive, they see how Melkor's presence would destroy the integrity of Ilúvatar's themes. Eventually, and with the aid of the Vala Tulkas, who enters Arda last, Melkor is temporarily overthrown, and the Valar begin shaping the world and creating beauty to counter the darkness and ugliness of Melkor's discordant noise.[T 3]  The Valar originally dwell on the Isle of Almaren in the middle of Arda, but after its destruction and the loss of the world's symmetry, they move to the western continent of Aman ("Unmarred"[1]) and found Valinor. The war with Melkor continues: The Valar realize many wonderful subthemes of Ilúvatar's grand music, while Melkor pours all his energy into Arda and the corruption of creatures like Balrogs, dragons, and Orcs. Most terrible of the early deeds of Melkor is the destruction of the Two Lamps and with them, the original home of the Valar, the Isle of Almaren. Melkor is captured and chained for many ages in the fastness of Mandos, until he is pardoned by Manwë.[T 3][T 4] With the arrival of the Elves in the world, a new phase of the regency of the Valar begins. Summoned by the Valar, many Elves abandon Middle-earth and the eastern continent for the West, Valinor, where the Valar concentrate their creativity. There they make the Two Trees, their greatest joy because they illuminate the beauty of Valinor and delight the Elves.[T 4] At Melkor's instigation the evil giant spider Ungoliant destroys the Trees. Fëanor, a Noldor Elf, with forethought and love, captures the light of the Two Trees in three Silmarils, the greatest jewels ever created. Melkor steals the Silmarils from Fëanor, kills his father, Finwë, chief of the Noldor in Aman, and flees to Middle-earth. Many of the Noldor, in defiance of the will of the Valar, swear revenge and set out in pursuit. This event, and the poisonous words of Melkor that foster mistrust among the Elves, leads to the exile of the greater part of the Noldor to Middle-earth: The Valar close Valinor against them to prevent their return.[T 5] For the remainder of the First Age, the Lord of Waters, Ulmo, alone of the Valar, visits the world beyond Aman. Ulmo directly influences the actions of Tuor, setting him on the path to find the hidden city of Gondolin.[T 6] At the end of the First Age, the Valar send forth a great host of Maiar and Elves from Valinor to Middle-earth, fighting the War of Wrath, in which Melkor is defeated. The lands are changed, and the Elves are again called to Valinor.[T 7] During the Second Age, the Valar's main deeds are the creation of Númenor as a refuge for the Edain, who are denied access to Aman but given dominion over the rest of the world. The Valar, now including even Ulmo, remain aloof from Middle-earth, allowing the rise to power of Morgoth's lieutenant, Sauron, as a new Dark Lord. Near the end of the Second Age, Sauron convinces the Númenóreans to attack Aman itself. This leads Manwë to call upon Ilúvatar to restore the world to order; Ilúvatar answers by destroying Númenor, as described in the Akallabêth.[T 8] Aman is removed from Arda (though not from the whole created world, Eä, for Elvish ships could still reach it).[T 8] In the Third Age, the Valar send the Istari (or wizards) to Middle-earth to aid in the battle against Sauron.[T 9]
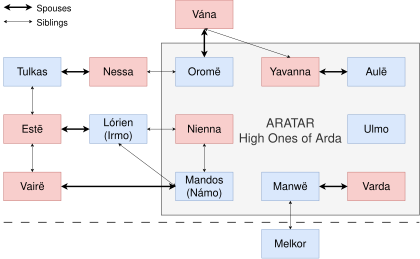
The chief ValarThe names and attributes of the chief Valar, as they are described in the "Valaquenta", are listed below. In Middle-earth, they are known by their Sindarin names: Varda, for example, is called Elbereth. Men know them by many other names, and sometimes worship them as gods. With the exception of Oromë, the names listed below are not actual names but rather titles: The true names of the Valar are nowhere recorded. The males are called "Lords of the Valar", and the females are called "Queens of the Valar," or Valier. Of the known seven male and seven female Valar, there are six married pairs: Ulmo and Nienna are the only ones who dwell alone. This is evidently a spiritual rather than a physical union, as in Tolkien's later conception they do not reproduce.[T 10] The Aratar (Quenya: Exalted), or High Ones of Arda, are the eight greatest of the Valar: Manwë, Varda, Ulmo, Yavanna, Aulë, Mandos, Nienna, and Oromë. Lórien and Mandos are brothers and are collectively called as the Fëanturi, "Masters of Spirits".[T 10] Ilúvatar brings the Valar (and all the Ainur) into being by his thought and may therefore be considered their father. However, not all the Valar are siblings; where this is held to be so, it is because they are so "in the thought of Ilúvatar". It was the Valar who first practise marriage and later pass on their custom to the Elves; all the Valar have spouses, save Nienna, Ulmo, and Melkor. Only one such marriage among the Valar takes place within the world, that of Tulkas and Nessa after the raising of the Two Lamps.[T 10] Lords
Queens
Ex-Valar
LanguageTolkien at first decided that Valarin, the tongue of the Valar, would be the proto-language of the Elves. He developed the Valarin language and its grammar in the early 1930s.[T 17] In this early conception, as described in the 1937 Lhammas, all Middle-earth's languages are derived from Valarin.[T 18] In the 1940s, he changed his mind, and the tongue he had developed became Primitive Quendian instead.[T 19] He then conceived an entirely new tongue for the Valar, still called Valarin; he did not develop this new language in any detail.[T 20] In this later conception, Valarin is unrelated to the other languages of Middle-earth. Only a few words of Valarin, mainly proper names, are recorded.[1] The Valar can communicate through thought and have no need for a spoken language, but may have developed Valarin when they took physical, humanlike (or elf-like) forms.[1] AnalysisBeowulfThe passage at the start of the Old English poem Beowulf about Scyld Scefing contains a cryptic mention of þā ("those") who have sent Scyld as a baby in a boat, presumably from across the sea, and to whom Scyld's body is returned in a ship funeral, the vessel sailing by itself. Shippey suggests that Tolkien may have seen in this both an implication of a Valar-like group who behave much like gods, and a glimmer of his Old Straight Road, the way across the sea to Valinor forever closed to mortal Men by the remaking of the world after Númenor's attack on Valinor.[2] Norse Æsir Scholars such as John Garth have noted that the Valar resemble the Æsir, the Norse gods of Asgard.[3] Thor, for example, physically the strongest of the gods, can be seen both in Oromë, who fights the monsters of Melkor, and in Tulkas, the strongest of the Valar. Manwë, the head of the Valar, has some similarities to Odin, the "Allfather",[4] while the wizard Gandalf, one of the Maiar, resembles Odin the wanderer.[5][6] Godlike powerTolkien compared King Théoden of Rohan, charging into the enemy at the Battle of the Pelennor Fields, to a Vala of great power, and to "a god of old":[T 21]
The Episcopal priest and author Fleming Rutledge comments that while Tolkien is not equating the events here with the Messiah's return, he was happy when readers picked up biblical echoes. In her view the language here is clearly biblical, evoking Malachi's messianic prophecy "See, the day is coming, burning like an oven, when all the arrogant and all evildoers will be stubble ... And you shall tread down the wicked, for they will be ashes under the soles of your feet".[7]
Pagan gods or angels The theologian Ralph C. Wood describes the Valar and Maiar as being what Christians "would call angels", intermediaries between the creator, Eru Ilúvatar, and the created cosmos. Like angels, they have free will and can therefore rebel against him.[8] Matthew Dickerson, writing in the J.R.R. Tolkien Encyclopedia, calls the Valar the "Powers of Middle-earth", noting that they are not incarnated and quoting the Tolkien scholar Verlyn Flieger's description of their original role as "to shape and light the world".[9] Dickerson writes that while Tolkien presents the Valar like pagan gods, he imagined them more like angels and notes that scholars have compared the devotion of Tolkien's Elves to Elbereth, an epithet of Varda, as resembling the Roman Catholic veneration of Mary the mother of Jesus. Dickerson states that the key point is that the Valar were "not to be worshipped".[9] He argues that as a result, the Valar's knowledge and power had to be limited, and they could make mistakes and moral errors. Their bringing of the Elves to Valinor meant that the Elves were "gathered at their knee", a moral error as it suggested something close to worship.[9] The scholar of literature Marjorie Burns notes that Tolkien wrote that to be acceptable to modern readers, mythology had to be brought up to "our grade of assessment". In her view, between his early work, The Book of Lost Tales,[c] and the published Silmarillion, the Valar had greatly changed, "civilized and modernized", and this had made the Valar "slowly and slightly" more Christian. For example, the Valar now had "spouses" rather than "wives", and their unions were spiritual, not physical. All the same, she writes, readers still perceive the Valar "as a pantheon", serving as gods.[10]
Elizabeth Whittingham comments that the Valar are unique to Tolkien, "somewhere between gods and angels". In her view they mostly lack the rough brutality of the Norse gods; they have the angels' "sense of moral rightness" but disagree with each other; and their statements most closely resemble those of Homer's Greek gods, who can express their frustration with mortal men, as Zeus does in the Odyssey[11] In a letter to Milton Waldman, Tolkien states directly that the Valar are "'divine', that is, were originally 'outside' and existed 'before' the making of the world. Their power and wisdom is derived from their Knowledge of the cosmogonical drama".[T 23] He explains that he intends them to be "of the same order of beauty, power, and majesty as the 'gods' of higher mythology".[T 23] Whittingham notes further that Tolkien likens lesser spirits, wizards, who are Maiar not Valar, to guardian angels; and that when describing the Maiar he "vacillates between 'gods' and 'angels' because both terms are close but neither is exactly right".[11] Tolkien states in another letter that the Valar "entered the world after its making, and that the name is properly applied only to the great among them, who take the imaginative but not the theological place of 'gods'."[T 24] Whittingham comments that the "thoughtful and carefully developed explanations" that Tolkien gives in these letters are markedly unlike his depictions of the Valar in his "earliest stories".[11]
Luck or providenceThe Tolkien scholar Tom Shippey discusses the connection between the Valar and "luck" on Middle-earth, writing that as in real life, "People ... do in sober reality recognise a strongly patterning force in the world around them" but that while this may be due to "Providence or the Valar", the force "does not affect free will and cannot be distinguished from the ordinary operations of nature" nor reduce the necessity of "heroic endeavour".[12] He states that this exactly matches the Old English view of luck and personal courage, as Beowulf's "wyrd often spares the man who isn't doomed, as long as his courage holds."[12] The scholar of humanities Paul H. Kocher similarly discusses the role of providence, in the form of the intentions of the Valar or of the creator, in Bilbo's finding of the One Ring and Frodo's bearing of it; as Gandalf says, they were "meant" to have it, though it remained their choice to co-operate with this purpose.[13] Rutledge writes that in The Lord of the Rings, and especially at moments like Gandalf's explanation to Frodo in "The Shadow of the Past", there are clear hints of a higher power at work in events in Middle-earth:[14]
Rutledge notes that in this way, Tolkien repeatedly hints at a higher power "that controls even the Ring itself, even the maker of the Ring himself [her italics]", and asks who or what that power might be. Her reply is that at the surface level, it means the Valar, "a race of created beings (analogous to the late-biblical angels)"; at a deeper level, it means "the One", Eru Ilúvatar, or in Christian terms, divine Providence.[15] Notes
ReferencesPrimary
Secondary
Sources
|
![Tolkien's Valar behave as a group, so that readers perceive them as a pantheon like the Olympian gods of the Greeks.[10]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/08/Raffaello%2C_concilio_degli_dei_02.jpg/707px-Raffaello%2C_concilio_degli_dei_02.jpg)
