|
Pterygoid processes of the sphenoid
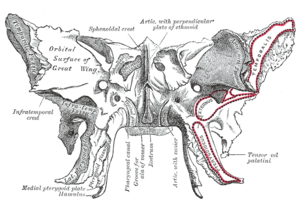
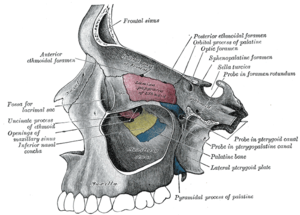
The pterygoid processes of the sphenoid (from Greek pteryx, pterygos, "wing"), one on either side, descend perpendicularly from the regions where the body and the greater wings of the sphenoid bone unite. Each process consists of a medial pterygoid plate and a lateral pterygoid plate, the latter of which serve as the origins of the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles. The medial pterygoid, along with the masseter allows the jaw to move in a vertical direction as it contracts and relaxes. The lateral pterygoid allows the jaw to move in a horizontal direction during mastication (chewing). Fracture of either plate are used in clinical medicine to distinguish the Le Fort fracture classification for high impact injuries to the sphenoid and maxillary bones. The superior portion of the pterygoid processes are fused anteriorly; a vertical groove, the pterygopalatine fossa, descends on the front of the line of fusion. The plates are separated below by an angular cleft, the pterygoid notch, the margins of which are rough for articulation with the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. The two plates diverge behind and enclose between them a V-shaped fossa, the pterygoid fossa, which contains the medial pterygoid muscle and the tensor veli palatini. Above this fossa is a small, oval, shallow depression, the scaphoid fossa, which gives origin to the tensor veli palatini. The anterior surface of the pterygoid process is broad and triangular near its root, where it forms the posterior wall of the pterygopalatine fossa and presents the anterior orifice of the pterygoid canal. In many mammals it remains as a separate bone called the pterygoid bone. Its name is Greek for "resembling a fin or wing", from its shape. Medial pterygoid plateThe medial pterygoid plate (or medial pterygoid lamina) of the sphenoid bone is a horse-shoe shaped process that arises from its underside. It is narrower and longer than the lateral pterygoid plate and curves lateralward at its lower extremity into a hook-like process, the pterygoid hamulus, around which the tendon of the tensor veli palatini glides. The lateral surface of this plate forms part of the pterygoid fossa, the medial surface constitutes the lateral boundary of the choana or posterior aperture of the corresponding nasal cavity. Superiorly the medial plate is prolonged on to the under surface of the body as a thin lamina, named the vaginal process, which articulates in front with the sphenoidal process of the palatine and behind this with the ala (wing) of the vomer. The angular prominence between the posterior margin of the vaginal process and the medial border of the scaphoid fossa is named the pterygoid tubercle, and immediately above this is the posterior opening of the pterygoid canal. On the under surface of the vaginal process is a furrow, which is converted into a canal by the sphenoidal process of the palatine bone, for the transmission of the pharyngeal branch of the internal maxillary artery and the pharyngeal nerve from the sphenopalatine ganglion. The pharyngeal aponeurosis is attached to the entire length of the posterior edge of the medial plate, and the constrictor pharyngis superior takes origin from its lower third. Projecting backward from near the middle of the posterior edge of this plate is an angular process, the processus tubarius, which supports the pharyngeal end of the Eustachian tube. The anterior margin of the plate articulates with the posterior border of the vertical part of the palatine bone. In many animals it is a separate bone called the pterygoid bone. Lateral pterygoid plate
The lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid (or lateral lamina of pterygoid process) is broad, thin, and everted and forms the lateral part of a horseshoe like process that extends from the inferior aspect of the sphenoid bone, and serves as the origin of the lateral pterygoid muscle, which functions in allowing the mandible to move in a lateral and medial direction, or from side-to-side. Its lateral surface forms part of the medial wall of the infratemporal fossa, and gives attachment to the lateral pterygoid muscle; its medial surface forms part of the pterygoid fossa, and gives attachment to the medial pterygoid muscle. Posterior edge is sharp, and often has sharp projection - pterygospinous process (Civinini process). References
External links
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||