|
Bootstrap aggregating
Bootstrap aggregating, also called bagging (from bootstrap aggregating) or bootstrapping, is a machine learning (ML) ensemble meta-algorithm designed to improve the stability and accuracy of ML classification and regression algorithms. It also reduces variance and overfitting. Although it is usually applied to decision tree methods, it can be used with any type of method. Bagging is a special case of the ensemble averaging approach. Description of the techniqueGiven a standard training set of size , bagging generates new training sets , each of size , by sampling from uniformly and with replacement. By sampling with replacement, some observations may be repeated in each . If , then for large the set is expected to have the fraction (1 - 1/e) (~63.2%) of the unique samples of , the rest being duplicates.[1] This kind of sample is known as a bootstrap sample. Sampling with replacement ensures each bootstrap is independent from its peers, as it does not depend on previous chosen samples when sampling. Then, models are fitted using the above bootstrap samples and combined by averaging the output (for regression) or voting (for classification).  Bagging leads to "improvements for unstable procedures",[2] which include, for example, artificial neural networks, classification and regression trees, and subset selection in linear regression.[3] Bagging was shown to improve preimage learning.[4][5] On the other hand, it can mildly degrade the performance of stable methods such as k-nearest neighbors.[2] Process of the algorithmKey TermsThere are three types of datasets in bootstrap aggregating. These are the original, bootstrap, and out-of-bag datasets. Each section below will explain how each dataset is made except for the original dataset. The original dataset is whatever information is given. Creating the bootstrap datasetThe bootstrap dataset is made by randomly picking objects from the original dataset. Also, it must be the same size as the original dataset. However, the difference is that the bootstrap dataset can have duplicate objects. Here is a simple example to demonstrate how it works along with the illustration below: Suppose the original dataset is a group of 12 people. Their names are Emily, Jessie, George, Constantine, Lexi, Theodore, John, James, Rachel, Anthony, Ellie, and Jamal. By randomly picking a group of names, let us say our bootstrap dataset had James, Ellie, Constantine, Lexi, John, Constantine, Theodore, Constantine, Anthony, Lexi, Constantine, and Theodore. In this case, the bootstrap sample contained four duplicates for Constantine, and two duplicates for Lexi, and Theodore. Creating the out-of-bag datasetThe out-of-bag dataset represents the remaining people who were not in the bootstrap dataset. It can be calculated by taking the difference between the original and the bootstrap datasets. In this case, the remaining samples who were not selected are Emily, Jessie, George, Rachel, and Jamal. Keep in mind that since both datasets are sets, when taking the difference the duplicate names are ignored in the bootstrap dataset. The illustration below shows how the math is done: ImportanceCreating the bootstrap and out-of-bag datasets is crucial since it is used to test the accuracy of a random forest algorithm. For example, a model that produces 50 trees using the bootstrap/out-of-bag datasets will have a better accuracy than if it produced 10 trees. Since the algorithm generates multiple trees and therefore multiple datasets the chance that an object is left out of the bootstrap dataset is low. The next few sections talk about how the random forest algorithm works in more detail. Creation of Decision TreesThe next step of the algorithm involves the generation of decision trees from the bootstrapped dataset. To achieve this, the process examines each gene/feature and determines for how many samples the feature's presence or absence yields a positive or negative result. This information is then used to compute a confusion matrix, which lists the true positives, false positives, true negatives, and false negatives of the feature when used as a classifier. These features are then ranked according to various classification metrics based on their confusion matrices. Some common metrics include estimate of positive correctness (calculated by subtracting false positives from true positives), measure of "goodness", and information gain. These features are then used to partition the samples into two sets: those who possess the top feature, and those who do not. The diagram below shows a decision tree of depth two being used to classify data. For example, a data point that exhibits Feature 1, but not Feature 2, will be given a "No". Another point that does not exhibit Feature 1, but does exhibit Feature 3, will be given a "Yes". This process is repeated recursively for successive levels of the tree until the desired depth is reached. At the very bottom of the tree, samples that test positive for the final feature are generally classified as positive, while those that lack the feature are classified as negative. These trees are then used as predictors to classify new data. Random ForestsThe next part of the algorithm involves introducing yet another element of variability amongst the bootstrapped trees. In addition to each tree only examining a bootstrapped set of samples, only a small but consistent number of unique features are considered when ranking them as classifiers. This means that each tree only knows about the data pertaining to a small constant number of features, and a variable number of samples that is less than or equal to that of the original dataset. Consequently, the trees are more likely to return a wider array of answers, derived from more diverse knowledge. This results in a random forest, which possesses numerous benefits over a single decision tree generated without randomness. In a random forest, each tree "votes" on whether or not to classify a sample as positive based on its features. The sample is then classified based on majority vote. An example of this is given in the diagram below, where the four trees in a random forest vote on whether or not a patient with mutations A, B, F, and G has cancer. Since three out of four trees vote yes, the patient is then classified as cancer positive.  Because of their properties, random forests are considered one of the most accurate data mining algorithms, are less likely to overfit their data, and run quickly and efficiently even for large datasets.[6] They are primarily useful for classification as opposed to regression, which attempts to draw observed connections between statistical variables in a dataset. This makes random forests particularly useful in such fields as banking, healthcare, the stock market, and e-commerce where it is important to be able to predict future results based on past data.[7] One of their applications would be as a useful tool for predicting cancer based on genetic factors, as seen in the above example. There are several important factors to consider when designing a random forest. If the trees in the random forests are too deep, overfitting can still occur due to over-specificity. If the forest is too large, the algorithm may become less efficient due to an increased runtime. Random forests also do not generally perform well when given sparse data with little variability.[7] However, they still have numerous advantages over similar data classification algorithms such as neural networks, as they are much easier to interpret and generally require less data for training.[citation needed] As an integral component of random forests, bootstrap aggregating is very important to classification algorithms, and provides a critical element of variability that allows for increased accuracy when analyzing new data, as discussed below. Improving Random Forests and BaggingWhile the techniques described above utilize random forests and bagging (otherwise known as bootstrapping), there are certain techniques that can be used in order to improve their execution and voting time, their prediction accuracy, and their overall performance. The following are key steps in creating an efficient random forest:
Algorithm (classification)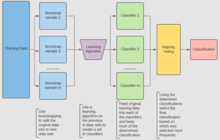 For classification, use a training set , Inducer and the number of bootstrap samples as input. Generate a classifier as output[12]
for i = 1 to m {
D' = bootstrap sample from D (sample with replacement)
Ci = I(D')
}
C*(x) = argmax #{i:Ci(x)=y} (most often predicted label y)
y∈Y
Example: ozone dataTo illustrate the basic principles of bagging, below is an analysis on the relationship between ozone and temperature (data from Rousseeuw and Leroy[clarification needed] (1986), analysis done in R). The relationship between temperature and ozone appears to be nonlinear in this dataset, based on the scatter plot. To mathematically describe this relationship, LOESS smoothers (with bandwidth 0.5) are used. Rather than building a single smoother for the complete dataset, 100 bootstrap samples were drawn. Each sample is composed of a random subset of the original data and maintains a semblance of the master set's distribution and variability. For each bootstrap sample, a LOESS smoother was fit. Predictions from these 100 smoothers were then made across the range of the data. The black lines represent these initial predictions. The lines lack agreement in their predictions and tend to overfit their data points: evident by the wobbly flow of the lines.  By taking the average of 100 smoothers, each corresponding to a subset of the original dataset, we arrive at one bagged predictor (red line). The red line's flow is stable and does not overly conform to any data point(s). Advantages and disadvantagesAdvantages:
Disadvantages:
HistoryThe concept of bootstrap aggregating is derived from the concept of bootstrapping which was developed by Bradley Efron.[15] Bootstrap aggregating was proposed by Leo Breiman who also coined the abbreviated term "bagging" (bootstrap aggregating). Breiman developed the concept of bagging in 1994 to improve classification by combining classifications of randomly generated training sets. He argued, "If perturbing the learning set can cause significant changes in the predictor constructed, then bagging can improve accuracy".[3] See also
References
Further reading
|












