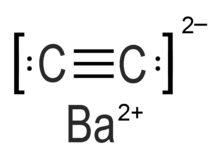|
Barium carbide
Barium carbide (also referred to as barium ethynediide or barium acetylide)[1] is a chemical compound in the carbide family having the chemical formula BaC2.[2] PreparationBarium carbide can be synthesized as an impure compound by reducing barium carbonate powder with metallic magnesium in the presence of carbon.[3] Barium carbide can also be made by reducing carbon dioxide with hot barium metal at 600°C.[4] These methods are used because of their high yield, and because the carbide is used to make acetylene. It can also be prepared by heating a barium amalgam and carbon powder mixture in a hydrogen current. The pure compound is prepared by reducing barium oxide with carbon at high temperature.[5] PropertiesBarium carbide reacts similarly to calcium carbide,[6] but it's more fusible. When exposed to extreme heat, the barium will evaporate leaving behind crystals of graphite. It can also absorb the carbon in a solution at high temperature.[5] HazardsBarium carbide can cause damage to the GI tract and irritation in the skin and eyes.[1] References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||