|
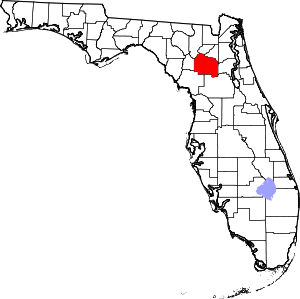
Alachua County, Florida
Alachua County (/əˈlætʃuə/ ⓘ ə-LATCH-oo-ə) is a county in the north central portion of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 278,468.[1] The county seat is Gainesville,[2] the home of the University of Florida. HistoryPrehistory and early European settlementsThe first people known to have entered the area of Alachua County were Paleo-Indians, who left artifacts in the Santa Fe River basin before 8000 BC. Artifacts from the Archaic period (8000 - 2000 BC) have been found at several sites in Alachua County. Permanent settlements appeared in what is now Alachua County around 100 AD, as people of the wide-ranging Deptford culture developed the local Cades Pond culture. The Cades Pond culture gave way to the Alachua culture around 600 AD.[3] The Timucua-speaking Potano tribe lived in the Alachua culture area in the 16th century, when the Spanish entered Florida. The Potano were incorporated by the colonists in the Spanish mission system, but new infectious diseases, rebellion, and raids by tribes backed by the English led to severe population declines. What is now Alachua County had lost much of its indigenous population by the early 18th century.[4] In the 17th century, Francisco Menéndez Márquez, Royal Treasurer for Spanish Florida, established the La Chua ranch on the northern side of what is now known as Payne's Prairie, on a bluff overlooking the Alachua Sink.[5] Chua may have been the Timucua language word for sinkhole. Lieutenant Diego Peña reported in 1716 that he passed by springs named Aquilachua, Usichua, Usiparachua, and Afanochua while traveling through what is now Suwannee County. In the twentieth-century, anthropologist J. Clarence Simpson assumed the named springs were in fact sinkholes.[6] The Spanish later called the interior of Florida west of the St. Johns River Tierras de la Chua, which became "Alachua Country" in English.[7] Around 1740, a band of Oconee people led by Ahaya, who was called "Cowkeeper" by the English, settled on what is now Payne's Prairie.[8] Ahaya's band became known as the Alachua Seminole. In 1774, botanist William Bartram visited Ahaya's town, Cuscowilla, near what Bartram called the Alachua Savanna. King Payne, who succeeded Ahaya as chief of the Alachua Seminole, established a new town known as Payne's Town. In 1812, during the Patriot War of East Florida, an attempt by American adventurers to seize Spanish Florida, a force of more than 100 volunteers from Georgia led by Colonel Daniel Newnan encountered a band of Alachua Seminole led by King Payne near Newnans Lake. After several days of intermittent fighting, Colonel Newnan's force withdrew. King Payne was wounded in the fight and died two months later. The Alachua Seminole then left Payne's Town and moved farther west and south, but other bands of Seminole moved in. A second American expedition in 1813 of U. S. Army troops and militia from Tennessee, led by Lt. Colonel Thomas Adams Smith, found some Seminoles, killing about 20, and burned every Seminole village they could find in the area.[9][10] In 1814, a group of more than 100 American settlers moved to a point believed to be near the abandoned Payne's Town (near present-day Micanopy) and declared the establishment of the District of Elotchaway of the Republic of East Florida. The settlement collapsed a few months later after its leader, Colonel Buckner Harris, was killed by Seminole. The remaining settlers returned to Georgia.[11] Early American settlements In 1817, F. M. Arredondo received the 20-mile square Arredondo Grant in the southern part of what is Alachua County. By the time Florida was formally transferred from Spain to the United States, people from the United States and from Europe were settling in the area. Wanton's Store, near the site of the abandoned King Payne's Town, attracted settlers, primarily from Europe, who founded Micanopy. The 1823 Treaty of Moultrie Creek required the Seminole to move a reservation south of what is now Ocala, and the flow of settlers into the area increased. Many settlers occupied former Seminole towns, such as Hogtown. Alachua County was created by the Florida territorial legislature in 1824. The new county stretched from the border with Georgia, south to Charlotte Harbor. The original county seat was Wanton's (per the store, as the name Micanopy had not been adopted). In 1828, the county seat was moved to Newnansville, near the current site of the city of Alachua.[11] As the area's population increased, Alachua County's size was reduced to organize new counties. In 1832, the county's northern part, including Newnansville, was separated to create Columbia County, forcing the county seat to move to various temporary locations, then to Spring Grove, from 1836 to 1839. In 1834, Hillsborough County was created, which included the area around Tampa Bay down to Charlotte Harbor. In 1839, that part of Columbia County south of the Santa Fe River was returned to Alachua County, and Newnansville was restored as the county seat. Hernando County was created in 1843 from that part of Alachua County south of the Withlacoochee River; Marion County was created in 1844; and Levy County was created in 1846 from that part of Alachua County west of the Suwannee River. It would be another 80 years before Alachua County was again reduced in size.[11] In 1853, the residents of Alachua County realized that the route of the planned Florida Railroad connecting Fernandina to Cedar Key would bypass Newnansville. A general meeting at Boulware Springs was called to consider moving the county seat to a new town on the expected route of the railroad. The motion to move the county seat was hotly contested by the residents of Newnansville, but Tillman Ingram, a plantation owner in Hogtown who owned a sawmill there, offered to build a courthouse in the new town. The offer was for such as favorable price that the move was approved. At tha time, the name "Gainesville" was chosen for the new town. The county seat was moved to Gainesville in late 1856, upon completion of the new courthouse.[12] Lynchings and disenfranchisementDuring the post-Reconstruction period, White Democrats regained control of the state legislature and worked to restore White supremacy. Violence against Blacks, including lynchings, rose in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as Whites imposed Jim Crow and discriminatory laws, disenfranchising most blacks, which forced them out of the political system. Alachua County was the site of 21 documented lynchings between 1891 and 1926.[13] The first three documented lynchings, in Gainesville in 1891, involved two Black men and a White man, who were associated with the notorious Harmon Murray.[14] Ten lynchings took place in Newberry, six of them in a mass lynching there in 1916.[13] These lynchings were conducted outside the justice system, by mobs or small groups working alone. Nineteen of the victims were Black; two were White.[15] (A 2015 report by the Equal Justice Initiative, based in Montgomery, Alabama, had identified 18 lynchings.[16] The Historical Commission documented three more, including two white men.)[15] In September 2017, the county commission approved plans to place markers with the names of the victims in the county. (See linked article for names of these individuals.)[15] They are working with the Historical Commission and cities to discuss how best to achieve this.[13] A state historical marker on the Newberry Lynchings was dedicated in 2019. Contemporary historyOn February 15, 2023, the board of county commissioners for Alachua County voted to support the proposed amendment to the Florida state constitution that is entitled, Florida Right To Clean And Healthy Waters, making Alachua the first county in the state to lend its support for adoption of the proposed amendment.[17] The proposed amendment is the subject of a statewide, nonpartisan campaign [18] to place adoption of it before all Florida voters on the 2024 ballot.[19] The adoption was signed into effect by its chair, Anna Prizzia, after a unanimous vote by the board. GeographyAccording to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 969 square miles (2,510 km2), of which 875 square miles (2,270 km2) is land and 94 square miles (240 km2) (9.7%) is water.[20] Adjacent counties
Demographics
As of the 2020 United States census, there were 278,468 people, 101,979 households, and 50,803 families residing in the county. As of the 2010 United States Census,[30] there were 247,336 people, 100,516 households, and 53,500 families residing in the county. There were 112,766 housing units in the county, an occupancy rate of 89.1%; of the occupied units, 54,768 (54.5%) were owner-occupied and 45,748 (45.5%) were renter-occupied. The population density was 282.91 per square mile (109.23/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 172,156 (69.9%) White, 50,282 (20.3%) Black or African American, 906 (0.3%) Native American, 13,235 (5.4%) Asian, 0.1% Pacific Islander, 1.7% from other races, and 2.6% from two or more races. 20,752 (8.4%) of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. Of the 100,516 households, 22.0% included children under the age of 18, 36.4% included a married husband and wife couple, 4.0% had a male head of house with no wife present, 12.8% had a female householder with no husband present, and 46.8% were non-families. 24.8% of all households included at least one child under the age of 18, and 19.6% included at least one member 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.32 and the average family size was 2.91. The demographic spread showed 17.9% under the age of 18 and 10.8% who were 65 years of age or older; 48.4% of the population identified as male and 51.6% as female. The median age was 30.1 years. The five year American Community Survey completed 2011 gave a median household income of $41,473 (inflation indexed to 2011 dollars) and a median family income of $63,435. Male full-time year round workers had a median income of $42,865, versus $36,351 for females. The per capita income for the county was $25,172; 23.6% of the population was living below the poverty line.[31] LanguagesAs of 2010[update], 86.43% of the population spoke English as their primary language, while Spanish was spoken by 6.38%, 1.18% spoke Chinese, 0.57% were speakers of Korean, and 0.52% spoke French as their native language.[32]  EducationThe Alachua County School District and its 47 institutions serve the entire county. Alachua County is also home to the University of Florida and Santa Fe College. LibraryThe Alachua County Library District is an independent special taxing district and the sole provider of public library service to approximately 250,000 citizens of Alachua County. This includes all of the incorporated municipalities in the county. It maintains a library headquarters and four branches in Gainesville. These locations include the Millhopper Branch in northwest Gainesville, the Tower Road Branch in unincorporated Alachua county southwest of Gainesville, the Library Partnership Branch in northeast Gainesville, and the Cone Park Branch in east Gainesville. The district also operates branches in the Alachua County municipalities of Alachua, Archer, Hawthorne, High Springs, Micanopy, Newberry, and Waldo, as well as a branch at the Alachua County Jail. The district's two bookmobiles visit more than 25 locations in the county from two to five times a month.[33][34][35] Library historyThe Alachua County Library District traces its origins to 1905, when the Twentieth Century Club in Gainesville started a subscription library. The Gainesville Public Library, a subscription library operated by the Library Association, opened in 1906. The Twentieth Century Club donated the books from its subscription library, and the new library also received books from the library of the East Florida Seminary, which had been absorbed by the newly founded University of Florida. The Gainesville Public Library became a free library in 1918, supported by funds from city taxes from all residents, but it was available only to whites. The building was constructed with the aid of a Carnegie library grant. The library became a department of the Gainesville municipal government in 1949. It was not until 1953 and opening of the Carver Branch Library that the city's African Americans had access to a library, as public facilities were still segregated. The Carver Branch closed in 1969, after the main library's desegregation. In 1958, the city of Gainesville and Alachua County agreed to jointly operate the library for the county. Branch libraries opened in High Springs, Hawthorne, and Micanopy the next year, and a bookmobile was put into service. Alachua County joined with Bradford County to operate the Santa Fe Regional Library. After Bradford County withdrew from the Regional Library, the Alachua County Library District was formally established in 1986. The Millhopper and Tower Road branches opened in 1992, and the branches in Alachua, Archer, Newberry, and Waldo were all opened by 1997. The Library Partnership Branch opened in 2009, and the Cone Park Branch in 2011. A new, permanent location for the Cone Park Branch Library opened near the Eastside Community Center in Gainesville on December 14, 2013.[36][37][38] TransportationMajor highwaysAirports
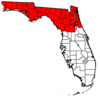
Politics and governmentStatewide electionsLike many other counties containing large state universities, Alachua County regularly supports the Democratic Party. It has voted for the Democratic candidate for president in the past eight elections. The county last supported a Republican presidential candidate in 1988, when it narrowly went for George H. W. Bush.
Voter registrationAs of May 31, 2024, the county had a Democratic Party plurality, with large Republican and independent minorities.[41]
County officesAlachua County is administered by the Alachua County Board of County Commissioners, a five-member legislative body. The Constitutional county-wide elected officials include the Clerk of the Court, the Supervisor of Elections, the Property Appraiser, the Sheriff, and the Tax Collector. The School Board and the Soil and Water Conservation District are also elected county-wide. Prior to 2024, county commissioners were elected at-large, but a ballot measure passed in 2022 created single-member district seats.
Law enforcementThe Alachua County Sheriff's Office is the chief law enforcement agency for unincorporated areas of Alachua County. As of 2023[update], the current sheriff is Emery Gainey, a Republican appointee of Governor DeSantis.[42] This marks the first time a Republican has controlled the sheriff's office since 2006.[43] This appointment came as a result of Sheriff Clovis Watson Jr. resigning due to health issues. In June 2007, ten employees in the sheriff's office, including the jail's director, were either fired or resigned while being investigated.[44] As of 2015[update] the sheriff's office had at least one Lenco BearCat armored vehicle and two helicopters provided by the federal government under various programs. The office received criticism after the BearCat was used in a routine traffic stop.[45] On August 9, 2021, a prison inmate, Erica Thompson, gave birth while being held in Alachua County Jail. Her baby died. Despite the mother's screams, jail staff did not provide or call for medical assistance. An investigation held that law enforcement did not violate any law or policy.[46] LandfillsAlachua County is the site of five closed landfills—Southwest Landfill, Southeast Landfill, Northwest Landfill, Northeast Landfill, and Northeast Auxiliary Landfill.[47] Since 1999, all solid waste from Alachua County has been hauled to the New River Solid Waste Facility in Raiford, in neighboring Union County.[48] Communities
Unincorporated communities
Historic communitiesAlachua County had a number of populated places, usually with a post office, established in the 19th century or early 20th century, but which were abandoned or had a much reduced population by the middle of the 20th century. Notable historic communities include:
See also
Notes
External linksWikimedia Commons has media related to Alachua County, Florida. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||