Non-metropolitan district in England
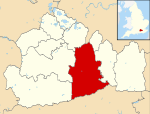
Mole Valley is a local government district in Surrey , England. Its council is based in Dorking , and the district's other town is Leatherhead . The largest villages are Ashtead , Fetcham and Great Bookham , in the northern third of the district.
Most of the district is on the escarpments of or adjoins the Surrey Hills , a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty , which cover parts of the North Downs and Greensand Ridge , including locally Leith Hill , Polesden Lacey and Box Hill . Denbies Wine Estate , the largest vineyard in the country, is on the hills north-west of Dorking.[ 2] Pilgrims' Way footpath runs along the North Downs. There are stations on the London –Worthing and Reading –Gatwick Airport railways, and in the northern third, a commuter stopping-service pattern line, London –Guildford (via Epsom) line.
The A24 road and the M25 motorway are the main thoroughfares and relative to London the incidence of car ownership is high. The area hosts hill-focussed sub-laps of the London–Surrey Classic cycling tour each year.
The neighbouring districts are Epsom and Ewell , Reigate and Banstead , Crawley , Horsham , Waverley , Guildford , Elmbridge and Kingston upon Thames , the latter being a London borough .
History
The district was created on 1 April 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972 , covering three former districts which were all abolished at the same time:[ 3] [ 4]
The new district was named after the River Mole , which flows through the area.[ 5]
Governance
South Holmwood Mole Valley District Council provides district-level services. County-level services are provided by Surrey County Council .[ 7] civil parishes , which form a third tier of local government for their areas.[ 8]
Political control
The council has been under Liberal Democrat majority control since 2019.
The first elections to the council were held in 1973, initially operating as a shadow authority alongside the outgoing authorities until the new arrangements came into effect on 1 April 1974. Political control of the council since 1974 has been as follows:[ 9] [ 10]
Leadership
The leaders of the council since 2012 have been:[ 11]
Composition
Following the 2024 election the composition of the council was:[ 13]
The next election is due in 2026.[ 14]
Elections
Since the last boundary changes in 2023 the council has comprised 39 councillors representing 13 wards , with each ward electing three councillors. Elections are held three years out of every four, with a third of the council (one councillor for each ward) elected each time for a four-year term of office. Surrey County Council elections are held in the fourth year of the cycle when there are no district council elections.[ 15]
Most of the district lies within the Mole Valley constituency , the exception being Ashtead which is within the Epsom and Ewell constituency .[ 8]
Premises
Pippbrook House: Council's offices until 1984. The council is based at Pippbrook on Reigate Road in Dorking, which was purpose-built for the council and opened in 1984.[ 16] [ 17]
Towns and parishes
The former Leatherhead Urban District, which included Ashtead , Fetcham , Great Bookham and Little Bookham , is an unparished area , as is the majority of the former Dorking Urban District.[ 8] [ 18]
The rest of the district is covered by civil parishes :[ 19] [ 20]
Demographics
A Legatum Prosperity Index published by the Legatum Institute in October 2016 showed Mole Valley as the second most prosperous council area in the United Kingdom, after the nearby Borough of Waverley .[ 21]
St Nicolas, Great Bookham St John, Wotton St Michael, Mickleham St Michael's Betchworth, 13th century, used in Four Weddings and a Funeral
Church
Place
Listed building
St Michael
Betchworth
I [ 22]
St Nicolas
Great Bookham
I[ 23]
All Saints
Little Bookham
II*
St Nicholas Charlwood
I[ 24]
St Michael
Mickleham
I [ 25]
St John the Evangelist
Wotton
I [ 26]
St Mary & St Nicholas
Leatherhead
II*[ 27]
St Barnabas
Ranmore Common
II* [ 28]
St Mary
Pixham
II* [ 29]
St Martin Dorking
II* [ 30]
St Mary
Fetcham
II* [ 31]
St Giles
Ashtead
II* [ 32]
St James
Abinger Common
II* [ 33]
Holy Trinity
Westcott
II* [ 34]
St Bartholomew
Leigh
II* [ 35]
St Margaret
Ockley
II* [ 36]
St John the Baptist
Walliswood
II* [ 37]
Emergency services
Mole Valley is served by these emergency services:
Surrey Police South East Coast Ambulance Service Surrey Fire & Rescue Service SURSAR Hospital NHS Hospital with no A&E . They are used for outpatients and rehabilitation.
Freedom of the District
See also
References
^ a b UK Census (2021). "2021 Census Area Profile – Mole Valley Local Authority (E07000210)" . Nomis . Office for National Statistics . Retrieved 5 January 2024 .^ "Government information about visitor attractions at Denbie's" . Surrey County Council. Archived from the original on 1 September 2012. Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ "The English Non-metropolitan District (Definition) Order 1972" , legislation.gov.uk The National Archives , SI 1972/2039, retrieved 17 November 2023 ^ "Charlwood and Horley Act 1974" , legislation.gov.uk The National Archives , 1974 c. 11, retrieved 13 January 2024 ^ "The English Non-metropolitan Districts (Names) Order 1973" , legislation.gov.uk The National Archives , SI 1973/551, retrieved 3 January 2024 ^ "Chairman of MVDC" . Mole Valley District Council . Retrieved 22 July 2024 .^ "Local Government Act 1972" , legislation.gov.uk The National Archives , 1972 c. 70, retrieved 31 May 2023 ^ a b c "Election Maps" . Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 9 January 2023 .^ "Compositions calculator" . The Elections Centre . Retrieved 9 September 2022 .^ "Mole Valley" . BBC News Online . Retrieved 7 May 2010 .^ "Council minutes" . Mole Valley District Council . Retrieved 15 July 2022 .^ Martin, Guy (25 May 2012). "Tory-independent union to continue in Mole Valley" . Surrey Live . Retrieved 15 July 2022 . ^ Van Klaveren, Tom (3 May 2024). "Mole Valley Local Election Results 2024 in full as Lib Dems maintain dominant position" . Surrey Live . Retrieved 22 July 2024 . ^ "Mole Valley" . Local Councils . Thorncliffe. Retrieved 22 July 2024 .^ "The Mole Valley (Electoral Changes) Order 2023" , legislation.gov.uk The National Archives , SI 2023/49, retrieved 13 January 2024 ^ "The war-time library goes up market into mansion" . Dorking and Leatherhead Advertiser . 14 February 1986. p. 16. Retrieved 13 January 2024 .^ "Dorking" . West Sussex Gazette . 10 December 1931. p. 4. Retrieved 13 January 2024 .^ "Surrey: Diagram showing administrative boundaries, 1971" . National Library of Scotland . Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 13 January 2024 .^ "Surrey County Council website" . Archived from the original on 3 September 2012. Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ "Parish Councils" . Mole Valley District Council . Retrieved 13 January 2024 .^ Braiden, Gerry (13 October 2016). "Scots authority named amongst UK's top 10 most prosperous – as neighbouring city props up table" . HeraldScotland . Retrieved 11 September 2020 . ^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1378131)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1028641)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1248610)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 15 July 2016 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1028835)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1294098)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1190429)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1189879)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1279086)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1028904)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1378187)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1028685)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1378082)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1227892)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1028748)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1028694)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Historic England . "Details from listed building database (1028844)" . National Heritage List for England . Retrieved 5 May 2012 .^ Martin, Guy (2 July 2013) [25 May 2010]. "Headley Court granted district's highest honour" . Surrey Live . Retrieved 3 May 2023 .
External links
Boroughs or districts Major settlements Topics
51°18′57.68″N 0°29′37.31″W / 51.3160222°N 0.4936972°W / 51.3160222; -0.4936972