|
Hohenzollern-Hechingen
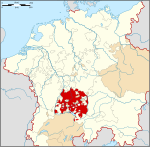
Hohenzollern-Hechingen (German: Fürstentum Hohenzollern-Hechingen) was a small principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to the Swabian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty. History The County of Hohenzollern-Hechingen was created in 1576, upon the partition of the County of Hohenzollern, a fief of the Holy Roman Empire. When the last count of Hohenzollern, Charles I of Hohenzollern (1512–1579) died, the territory was to be divided up between his three sons:
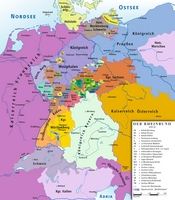
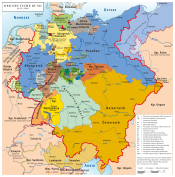
Unlike the Hohenzollerns of Brandenburg and Prussia, the Hohenzollerns of southwest Germany remained Roman Catholic. The county was raised to a principality in 1623. The main seat was the Friedrichsburg castle in Hechingen. The principality joined the Confederation of the Rhine in 1806 and was a member state of the German Confederation between 1815 and 1850. The democratic Revolution of 1848 was relatively successful in Hohenzollern, and on 16 May 1848, the Prince was forced to accept the establishment of a constitution. However, the conflict between monarch and democrats continued, and on 6 August 1849, Hohenzollern was occupied by Prussian forces. On 7 December 1849, Prince Constantine sold the country to his relative, King Frederick William IV of Prussia. On 12 March 1850, Hohenzollern-Hechingen officially became part of Prussia, and formed together with Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen the Province of Hohenzollern. Rulers Counts of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1576–1623)Source:[3][better source needed]
Princes of Hohenzollern-Hechingen (1623–1850)
References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||